Shin Splints, medically termed as Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS), is associated with overuse of the legs, and refers to pain in the region between the knee and the ankle. Shin Splint injuries commonly occur in athletes, especially runners.
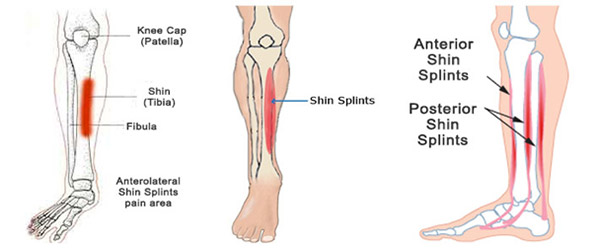
(From: http://www.foothealthclinic.com.au/conditions/foot-ankle-pain/shin-splints/)
Symptoms of Shin Splints
- Pain in front of outer leg below the knee and above the ankle
- Pain can be relieved after rest, but recurs when resuming running activities
- Pain can be severe enough to halt activities
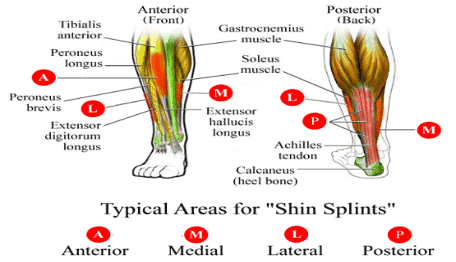
(From: http://runlikecrazy.com/2014/06/02/shin-splints/)
Causes of Shin Splints
Shin Splints are caused by:
Repeated micro-trauma to the muscles surrounding the tibia (shin bone)
Overuse of muscles of the lower extremities
Biomechanical irregularities (mostly excessive pronation)
Tight calf muscles
Weak ankles
Treatment of Shin Splints
Plantar fasciitis is a complex condition that often requires tailored treatment that should be developed in consultation with a Health Professional. There are a range of treatment options available such as:
- Rest – It is recommended to not train beyond the “pain barrier” of the injury as further activity can worsen the condition.
- Over-the-counter orthotic footwear to control foot over pronation (this cost-effective solution applies to most people). For those with foot over supination (foot rolls outwards) a podiatrist or chiropractor may need to be consulted for a pair of prescribed orthotic insoles.
- Deep tissue massage can be effective to relieve tight calf muscles as well as help break down any adhesions.
- Acupuncture is believed to be effective to significantly reduce the pain and inflammation. There is also evidence it helps break down any adhesions.
- Exercises to strengthen the ankles.
Stress fractures may develop if shin splint injuries are left untreated.
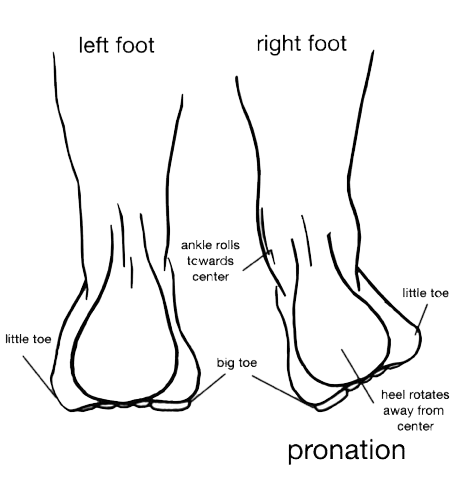
(From: https://www.orthoticshop.com/over-pronation-insoles/)
